Overloading while EV charging can occur when the power drawn by your charging system exceeds the amount of power that has been ordered. This can be caused by a number of factors, including charging multiple EVs at once, charging during peak energy demand times, or using a charging system that is not designed to handle high power loads.
Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to prevent overloading while EV charging. One solution is to invest in a charging system that is designed to handle high power loads, such as a DC fast charger. These chargers are capable of delivering high levels of power quickly and efficiently, reducing the risk of overloading.
Another solution is to stagger your charging times to avoid charging multiple EVs at once. This can help to spread out the power load and reduce the risk of overloading. Additionaly, charging during off-peak hours can help to reduce the risk of overloading,, as energy demand is typically lower during these times.
Table of contents:
- Understanding the Causes of Overloading While EV Charging
- Investing in a Charging System That Can Handle High Power Loads
- Staggering Charging Times to Reduce the Risk of Overloading
- Charging During Off-Peak Hours to Reduce Energy Demand
- Case Study: How a Company Prevented Overloading While EV Charging by Monitoring and Managing their Power Load
Understanding the Causes of Overloading While EV Charging
Overloading can be caused by a variety of factors, including the power requirements of the charging system, the power available at the charging location, and the power requirements of the electric vehicle being charged.
One common cause of overloading is charging multiple EVs at once. This can put a strain on the charging system and cause it to draw more power than is available. To prevent overloading in this situation, it’s important to stagger charging times or invest in a charging system that is designed to handle multiple EVs simultaneously.
Another cause of overloading is charging during peak energy demand times. During these times, the available power supply may be limited, making it difficult for your charging system to draw the power it needs. To avoid overloading during peak times, it’s recommended to charge during off-peak hours when energy demand is lower.
The power requirements of the charging system itself can also cause overloading. Charging systems that are not designed to handle high power loads can put a strain on the available power supply and cause overloading. To prevent this, it’s important to invest in a charging system that is designed to handle the power requirements of your electric vehicle and the EMS system.
Investing in a Charging System That Can Handle High Power Loads
Charging systems that are not designed to handle high power loads can put a strain on the available power supply and cause overloading, which can damage the charging system and lead to costly repairs.
To prevent overloading (in case of charging station), it’s important to invest in a charging system that is designed to handle the power requirements of your electric vehicle. One solution is to invest in a DC fast charger, which is capable of delivering high levels of power quickly and efficiently. These chargers are designed to handle high power loads, reducing the risk of overloading and ensuring that your electric vehicle is charged quickly and efficiently.
Overloading can be a concern for businesses and cities that have large fleets of electric vehicles, as the power demand required to charge multiple vehicles simultaneously can exceed the available power supply. To prevent overloading, it’s important to invest in a charging system that is designed to handle high power loads and to stagger charging times to spread out the power load.
In addition, not having enough energy to power electric vehicles can be a concern for businesses and cities, particularly during periods of high energy demand or when renewable energy sources are not producing enough power. To address this issue, it’s important to invest in energy storage solutions like batteries, which can store excess energy generated during periods of high renewable energy production and use it to power electric vehicles during periods of low production.
Overall, electric city buses and EV car fleets offer a range of benefits, but they also pose unique challenges when it comes to overloading and not having enough energy. By investing in a charging system that is designed to handle high power loads, staggering charging times, and investing in energy storage solutions like batteries, businesses and cities can ensure that their electric vehicle fleets are charged efficiently and reliably.
Staggering Charging Times to Reduce the Risk of Overloading
Staggering charging times is an effective way to reduce the risk of overloading while EV charging. This involves spreading out the charging times of multiple electric vehicles to avoid charging them alll at once, which can put a strain on the available power supply and cause overloading.
To stagger charging times, it’ s important to have a clear understanding of the power requirements of each electric vehicle and the power available at the charging location. This information can be used to create a charging schedule that spreads out the charging times of multiple electric vehicles, reducing the risk of overloading and ensuring that each vehicle is charged efficiently.
Staggering charging times can also help to reduce the demand on the power grid during peak energy demand times, as charging can be scheduled during off-peak hours when energy demand is lower. This can help to reduce the strain on the available power supply and prevent overloading while also supporting sustainable energy practices.
Overall, staggering charging times is an effective way to reduce the risk of overloading while EV charging. By working with an EV charging expert and creating a charging schedule that spreads out the charginng times of multiple electric vehicles, businesses and individuals can ensure that their charging system runs smoothly and efficiently, and that they are supporting sustainable energy practices.
Charging During Off-Peak Hours to Reduce Energy Demand
Charging during off-peak hours is an effective way to reduce energy demand and prevent overloading while EV charging. Off-peak hours refer to times of the day when energy demand is lower, typically outside of peak hours during the day when energy demand is at its highest.
By charging during off-peak hours, businesses and individuals can reduce the strain on the available power supply and prevent overloading. This can help to ensure that electric vehicles are charged efficiently and reliably without risking damage to the charging system.
Charging during off-peak hours can also help to support sustainable energy practices by reducing the demand for energy during peak hours. This can help to reduce the reliance on non-renewable energy sources and support the growth of renewable energy technologiess.
To effectively charge during off-peak hours, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the energy demand at the charging location and the peak hours for energy demand. This information can be used to create a charging schedule that maximizes the use of off-peak hours while ensuring that electric vehicles are charged efficiently.
To further support charging during off-peak hours, businesses and individuals can invest in renewable energy technologies like solar panels with EMS, which can generate energy during peak hours and store excess energy in batteries for use during off-peak hours.
Case Study: How a Company Prevented Overloading While EV Charging by Monitoring and Managing their Power Load
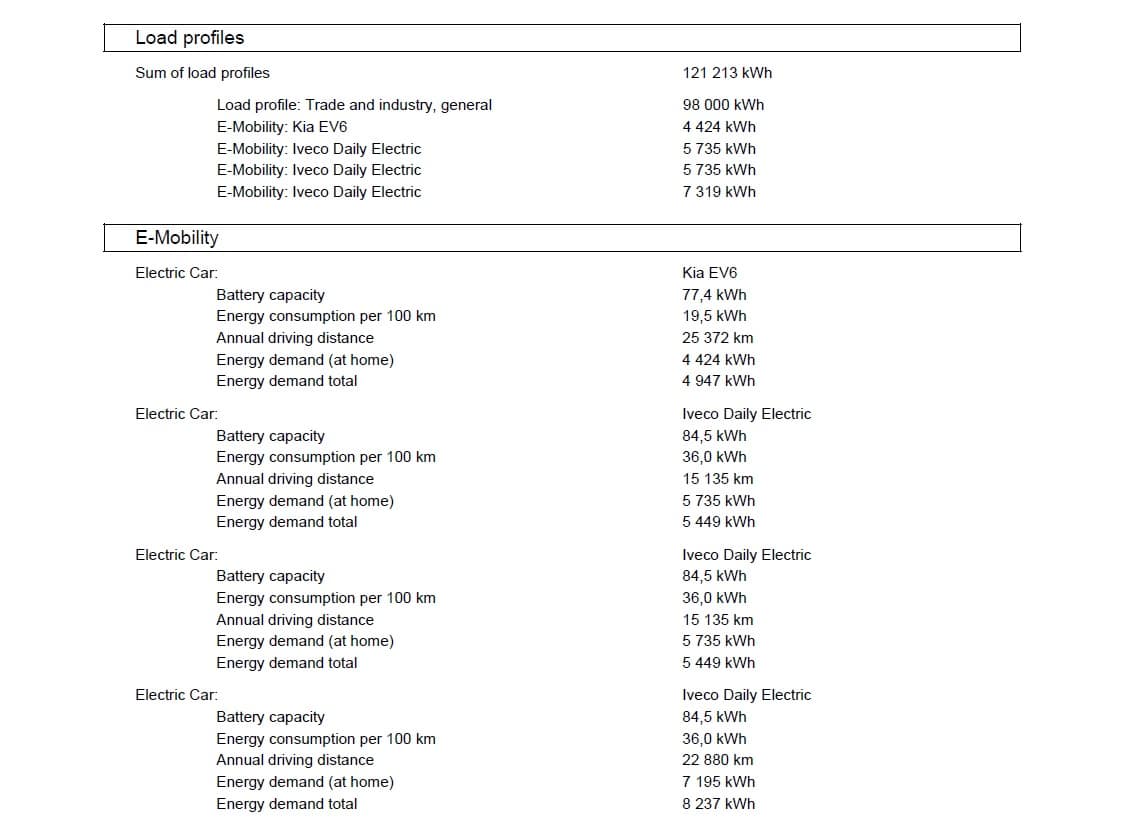
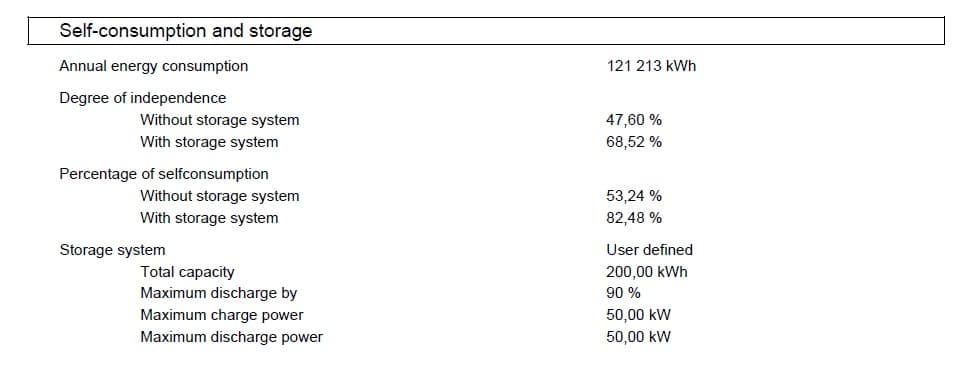
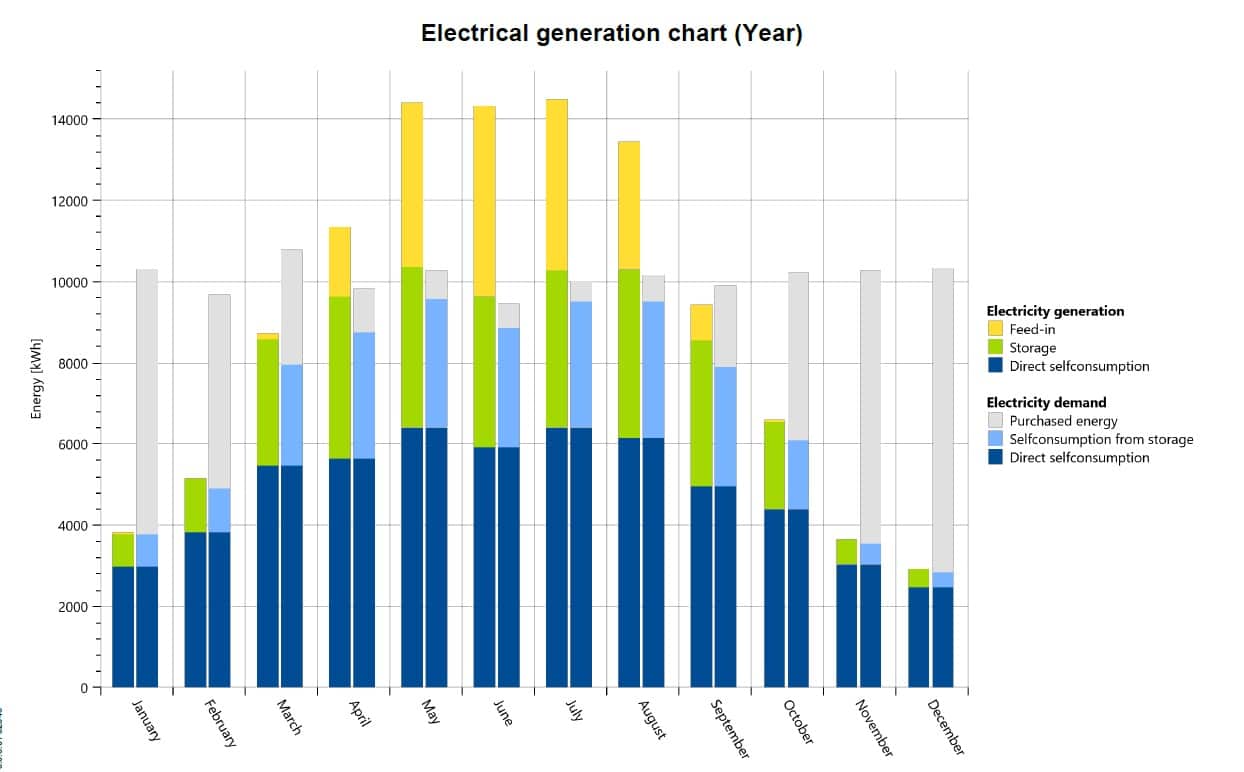
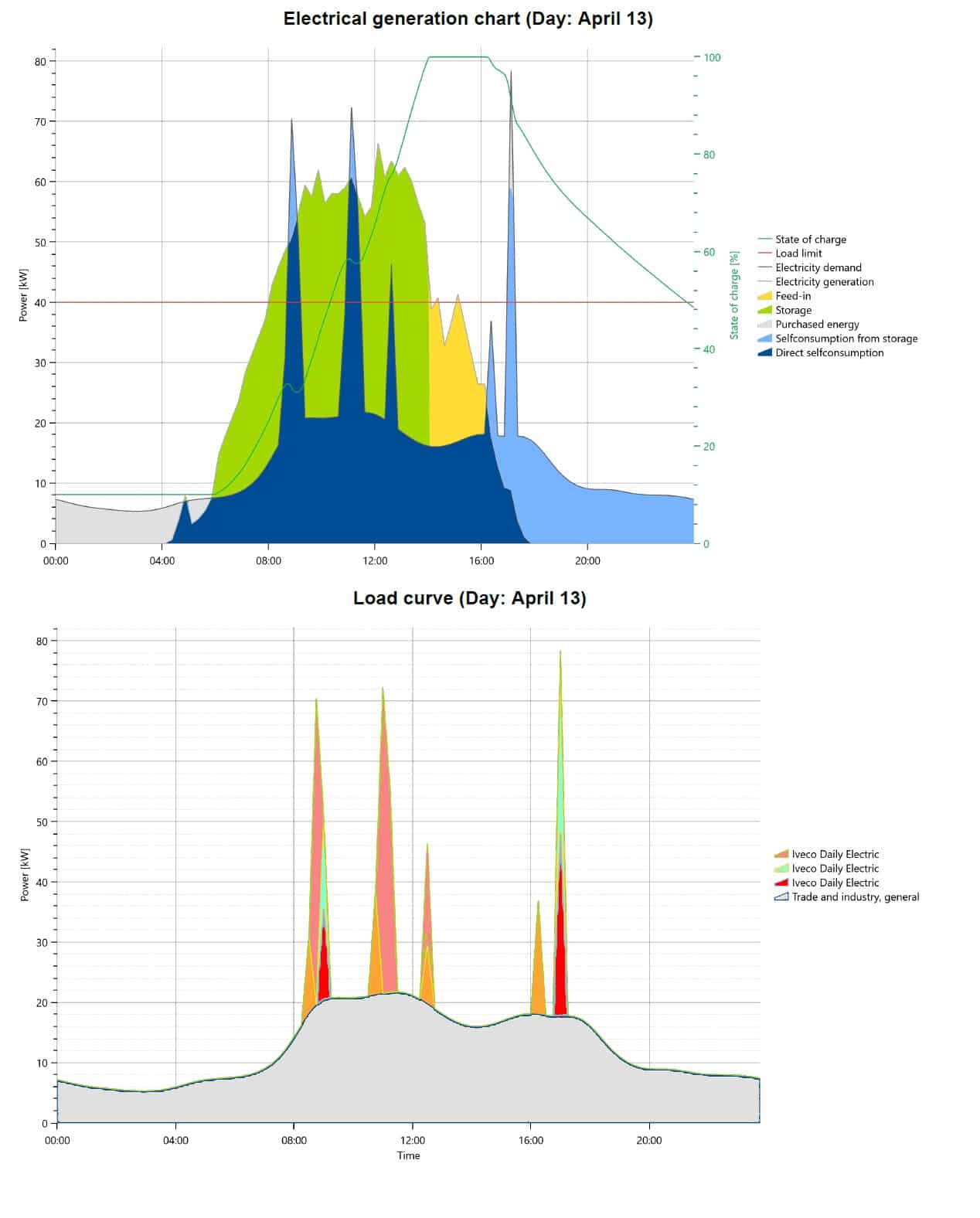
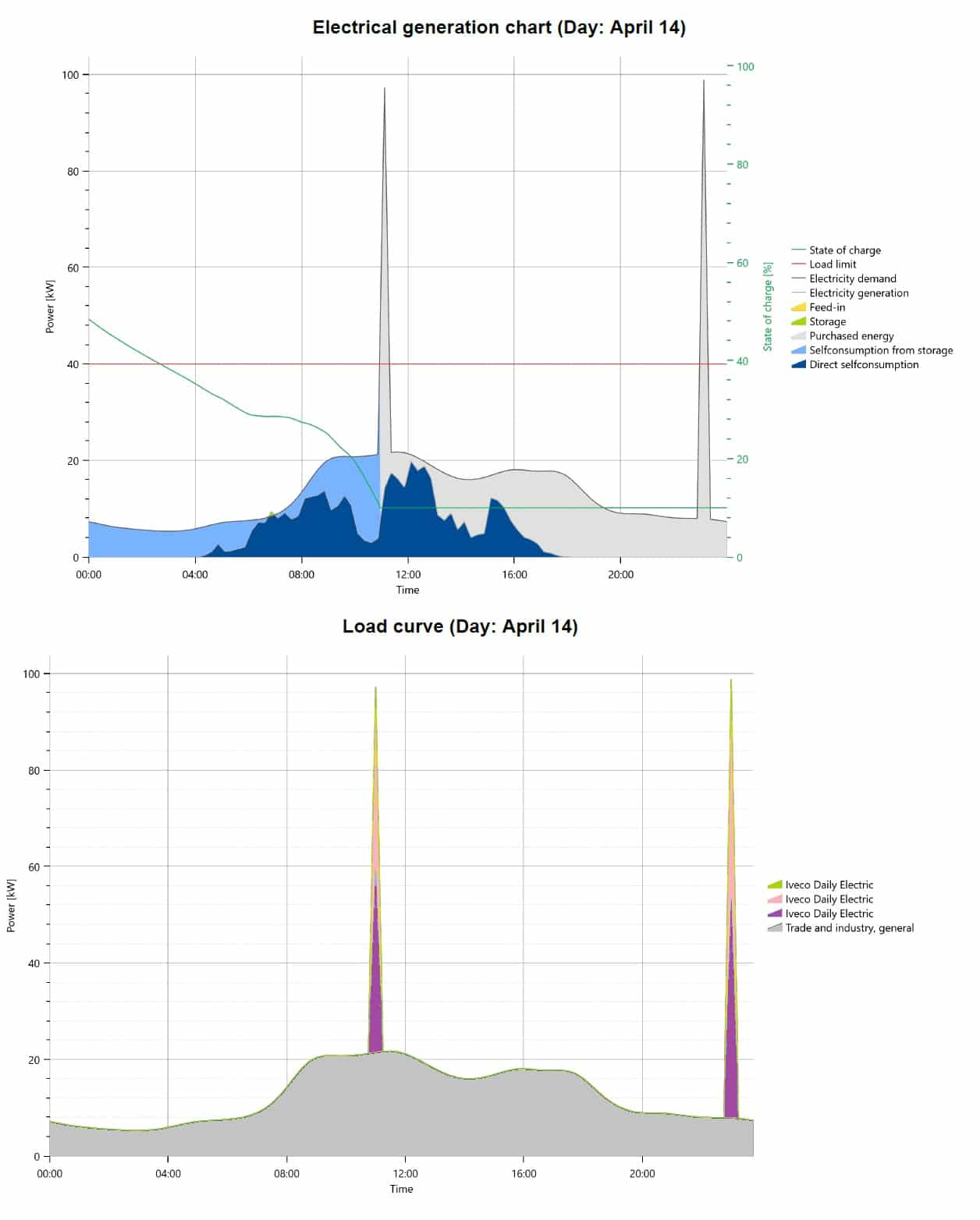
On April 14th, a company with one Kia EV and three Iveco Daily Electrics experienced overloading during EV charging due to low solar production and an empty energy storage system. The company owns a 103 kWp solar system and a 50 kW 200 kWh energy storage system. An annual energy usage of 121,213 kWh, the company’s ordered energy was only 40 kW, due to poor grid in this location.
Due to the low solar production on April 14th, the company had to rely on grid power to charge their electric vehicles. The high power demand from the EV charging, combined with the low ordered energy, led to overloading and a strain on the available power supply.
To prevent overloading in the future, the company implemented a charging schedule that staggered the charging times of their electric vehicles and avoided charging during peak energy demand times. They also invested in additional energy storage capacity to ensure that they have enough energy available to power their electric vehicles during periods of low solar production.
Without the energy storage system, the company had a percentage of self-consumption of 53.24%, while with the energy storage system, the percentage of self-consumption increased to 82.48%.
Overall, this case study highlights the importance of investing in energy storage solutions and implementing effective charging schedules to prevent overloading during EV charging, even for companies with a small fleet of electric vehicles.
Overloading and exceeding the ordered energy limit during EV charging can lead to a range of consequences, including:
- Damage to the charging system: Overloading can cause damage to the charging system, potentially leading to costly repairs or replacements
- Increased electricity bills: Exceeding the ordered energy limit can result in higher electricity bills, as the company may be charged for the excess energy usage!!!
- Reduced battery life: Overloading and charging at high power levels can reduce the lifespan of electric vehicle batteries, which can be expensive to replace.
- Safety hazards: Overloading can create safety hazards, includinng overheating and electrical fires, which can put people and property at risk.
- Inconvenience: Overloading and exceeding the ordered energy limit can cause disruptions and inconvenience, as charging times may need to be rescheduled or delayed
- Power outages: Overloading can cause power outages, disrupting not just the charging of electric vehicles, but also other critical systems and appliances that rely on electricty.
- Reduced charging efficiency Overloading can cause charging efficiency to decrease, resulting in longer charging times and reduced range for electric vehicles.
- Increased maintenance costs: Overloading and exceeding the ordered energy limit can lead to increased maintenance costs for charging systems and electric vehicles, potentialy requiring more frequent repairs and replacements.
- Negative environmental impact: Overloading and exceeding the ordered energy limit can result in the increased use of non-renewable energy sources, leading to a negative environmental impact and contributing to climate change
- Decreased customer satisfaction: Overloading and exceeding the ordered energy limit can lead to decreased customer satisfaction, as electric vehicle owners may experience delays or interruptions in their charging, impacting their ability to use their vehicles as needed.


