As the world seeks sustainable and reliable energy solutions, microgrids are emerging as game-changers in the energy landscape. These decentralized energy systems offer numerous benefits, from increased resilience to cost savings and reduced carbon emissions. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of microgrids, exploring their applications, technologies, and how they can empower communities with energy independence.
What is a Microgrid?
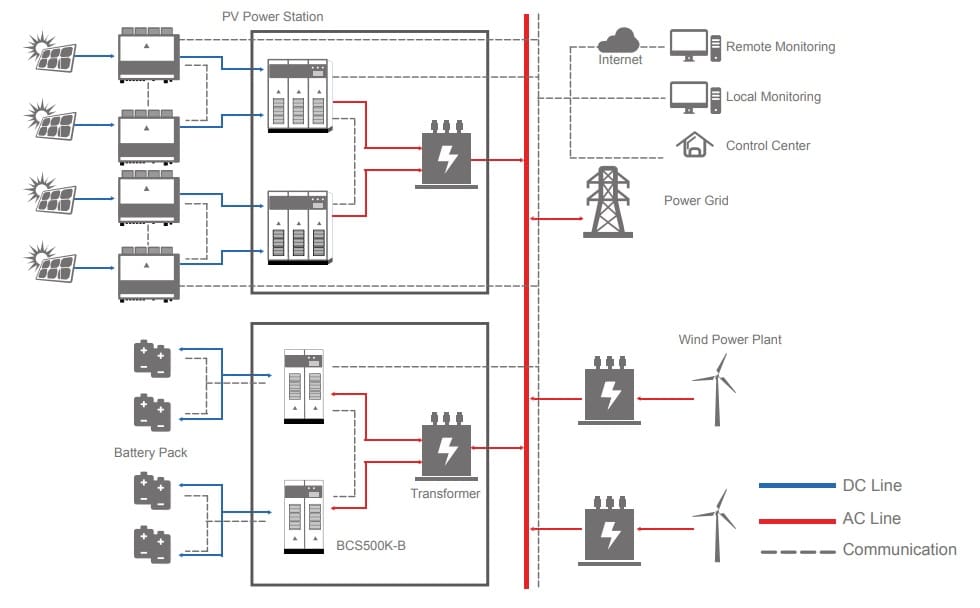
A microgrid is a localized energy system that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main power grid. They typically consist of distributed energy resources (DERs), such as solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems, along with the necessary control and management systems. Microgrids can seamlessly switch between grid-connected and off-grid operation, providing energy resilience and flexibility.
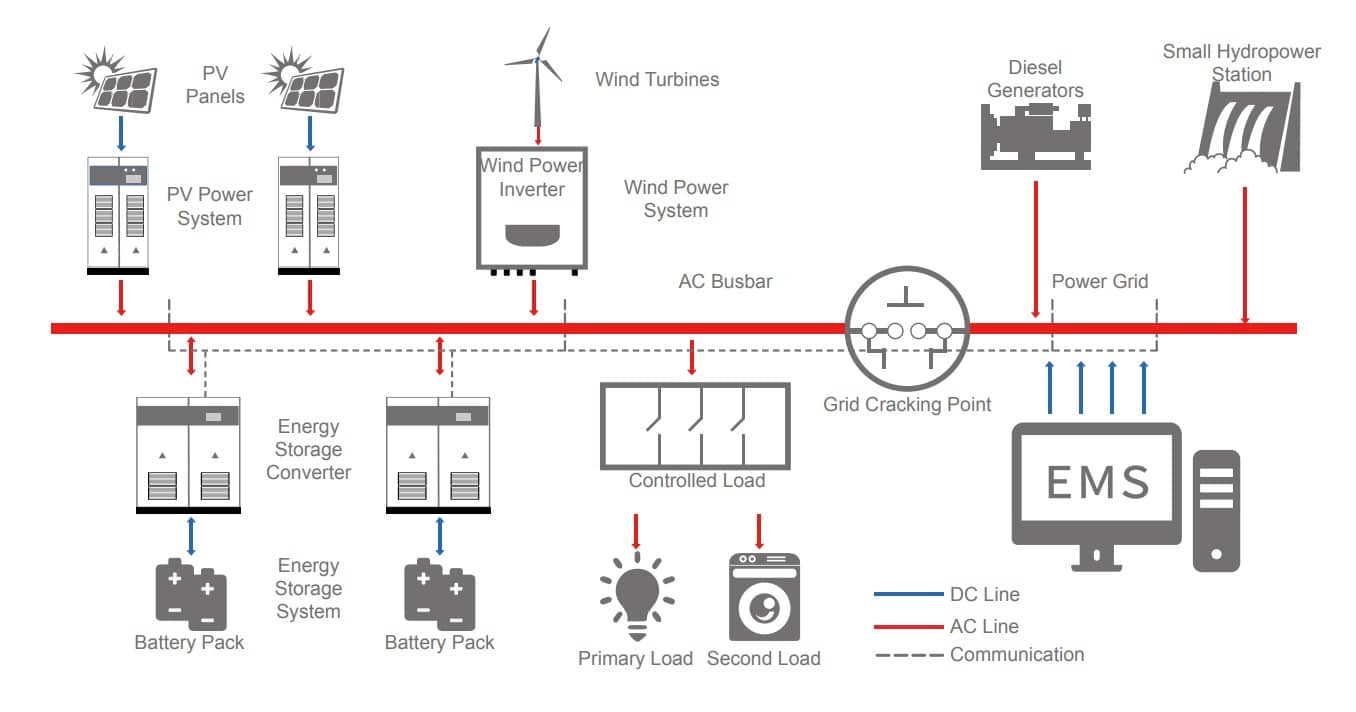
Key Components of a Microgrid
- Distributed Energy Resources (DERs): These include renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, as well as conventional generators and energy storage systems.
- Energy Storage: Microgrids often incorporate battery storage to store excess energy and ensure a stable supply during periods of high demand or low generation.
- Energy Management System (EMS): This system monitors, controls, and optimizes the operation of the microgrid, balancing energy supply and demand while maintaining grid stability.
- Switching and Control Systems: These systems enable the microgrid to operate in parallel with the main grid or in islanded mode, ensuring seamless transition between grid-connected and off-grid operation.
Benefits of Microgrids
Resilience and Reliability
Microgrids provide a stable and reliable power supply, even during grid outages or extreme weather events. They can maintain critical services and reduce the impact of power disruptions on local communities.
Energy Independence
By generating and storing energy locally, microgrids empower communities to become less reliant on the main power grid. This energy independence can lead to cost savings and improved energy security.
Sustainability
Microgrids facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, reducing carbon emissions and promoting a cleaner energy future.
Cost Savings
By optimizing energy consumption and reducing reliance on the main power grid, microgrids can help communities save on energy costs and lower peak demand charges.
Applications of Microgrids
Microgrids have a wide range of applications, including:
- Rural and Remote Communities: Microgrids can provide reliable, clean energy to areas with limited or no access to the main power grid, fostering sustainable development and improving living standards.
- Commercial and Industrial Facilities: Businesses can utilize microgrids to optimize energy consumption, reduce peak demand charges, and enhance energy reliability.
- Military Bases and Critical Infrastructure: Microgrids can ensure a stable power supply to critical facilities, enhancing security and reducing vulnerability to grid disruptions.
- Campuses and Institutions: Educational and research institutions can benefit from microgrids by lowering energy costs, improving sustainability, and providing opportunities for research and innovation.
Microgrid Technologies and Solutions
Several innovative technologies and solutions are driving the growth and adoption of microgrids:
- Smart Microgrid Management Systems: These advanced systems use real-time data and analytics to optimize the operation of the microgrid, maximizing efficiency and reliability.
- Grid-Connected Microgrids: These microgrids can seamlessly integrate with the main power grid, providing grid support services and ensuring a stable energy supply.
- Scale Microgrid Solutions These solutions are designed for easy scalability, allowing communities and businesses to expand their microgrid infrastructure as their energy needs grow.
- Microgrid-as-a-Service (MaaS): MaaS is an innovative business model that allows customers to access the benefits of a microgrid without the upfront capital investment, by partnering with microgrid companies that design, build, and operate the system on their behalf.
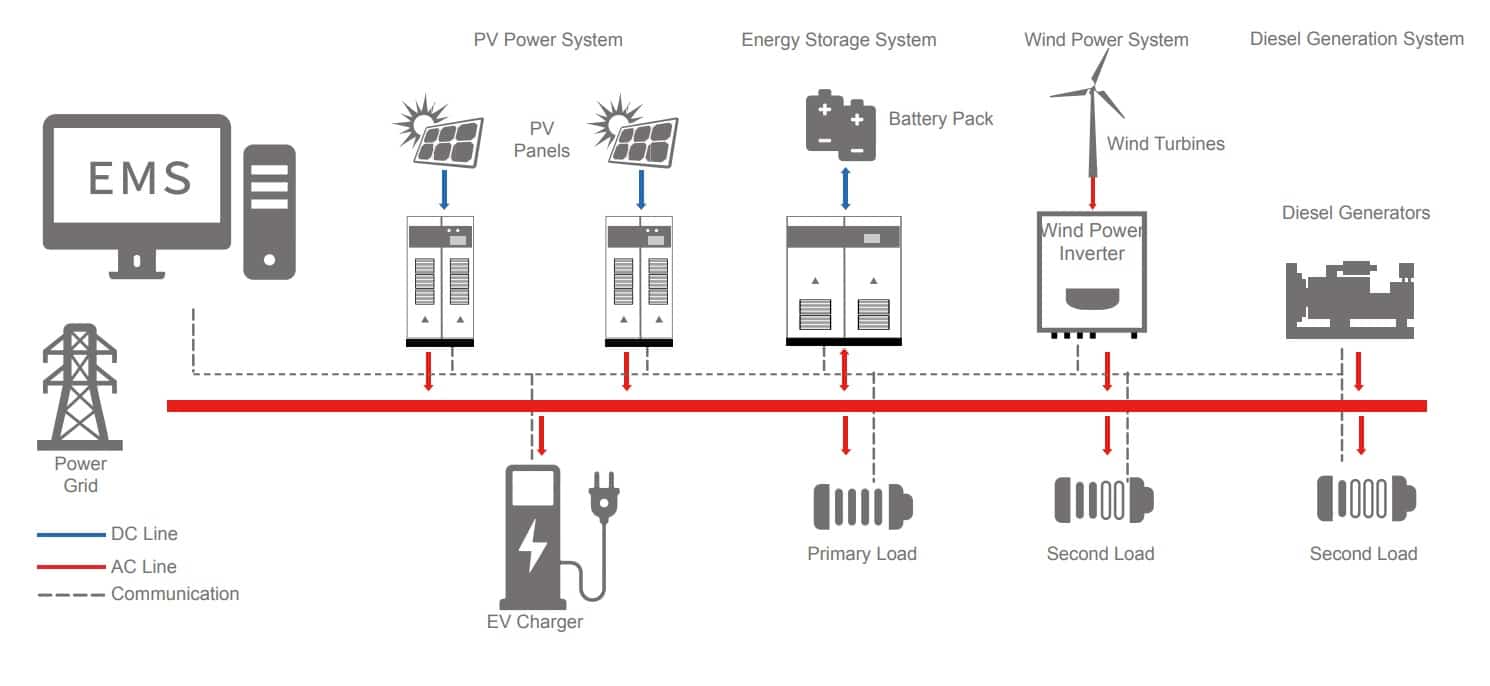
The Future of Microgrids
As the world continues to embrace renewable energy and decentralized power systems, microgrids are poised to play an increasingly important role in the global energy landscape. Their ability to provide energy resilience, independence, and sustainability makes them a crucial component of the transition to a cleaner, more efficient energy future.
By adopting microgrid technology, communities and businesses can unlock the potential of distributed energy resources and take control of their energy destiny. As advancements in energy storage and smart grid management systems continue, the capabilities and benefits of microgrids will only grow, further accelerating their adoption and impact.
Ready to explore the world of microgrids further? Check out our comprehensive guide on cutting-edge battery technologies and learn how they’re transforming the way we store and manage energy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a microgrid? A: A microgrid is a localized energy system that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main power grid. It typically consists of distributed energy resources (DERs), energy storage systems, and control and management systems. Q: What are the benefits of microgrids? A: Microgrids offer several benefits, including increased resilience and reliability, energy independence, sustainability, and cost savings. Q: Can microgrids operate off-grid? A: Yes, microgrids can operate in off-grid or “islanded” mode, providing energy to their local loads without relying on the main power grid. Q: What are some applications of microgrids? A: Microgrids have a wide range of applications, including rural and remote communities, commercial and industrial facilities, military bases and critical infrastructure, and campuses and institutions. Q: How do microgrids integrate renewable energy sources? A: Microgrids can incorporate renewable energy sources like solar and wind power through their distributed energy resources (DERs), promoting a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. Q: What are some emerging microgrid technologies and solutions? A: Emerging microgrid technologies and solutions include smart microgrid management systems, grid-connected microgrids, scale microgrid solutions, and Microgrid-as-a-Service (MaaS) business models.Q: Can a microgrid save money on energy costs?
A: Yes, microgrids can help save money on energy costs by optimizing energy consumption, reducing reliance on expensive grid electricity, and enabling participation in demand response and other energy market programs.
Q: How are microgrids controlled and managed?
A: Microgrids are controlled and managed by advanced microgrid management systems that use real-time data and analytics to optimize energy generation, storage, and consumption, ensuring reliable and efficient operation.
Q: What types of energy storage systems can be integrated into a microgrid?
A: Microgrids can integrate various energy storage systems, including battery energy storage systems (BESS), flywheels, and pumped hydro storage, depending on the specific needs and requirements of the microgrid.
Q: Are microgrids environmentally friendly?
A: Microgrids can be environmentally friendly when they incorporate renewable energy sources like solar and wind power and use efficient energy storage and management systems to minimize their carbon footprint.
Q: Can a microgrid provide backup power during a grid outage?
A: Yes, a microgrid can provide backup power during a grid outage by disconnecting from the main power grid and operating in islanded mode, ensuring a continuous and reliable supply of electricity for its local loads.
Q: Can a microgrid on an island incorporate a diesel generator?
A: Yes, a microgrid on an island can incorporate a diesel generator as a backup or supplementary power source. By combining diesel generation with renewable energy sources like solar PV and wind, the microgrid can optimize its energy mix and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Q: Can a microgrid on an island support electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure?
A: Yes, a microgrid on an island can support electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure. By integrating EV chargers into the microgrid, the system can efficiently manage energy consumption and optimize charging times to minimize peak demand and reduce overall energy costs.
Q: How can solar PV be integrated into an island microgrid?
A: Solar PV can be integrated into an island microgrid through the installation of solar panels, which can be mounted on rooftops, ground-mounted arrays, or floating installations. The solar energy generated by the PV panels is then converted into electricity and used to power the microgrid’s loads or stored in an energy storage system for later use.
Q: How can wind generators be integrated into an island microgrid?
A: Wind generators can be integrated into an island microgrid by installing wind turbines at suitable locations on the island, where wind resources are abundant and consistent. The electricity generated by the wind turbines is then distributed through the microgrid to power local loads or stored in an energy storage system for future use.
Q: How can an island microgrid balance the energy supply from different sources?
A: An island microgrid can balance the energy supply from different sources using advanced control and management systems that optimize energy generation, storage, and consumption in real-time. These systems use data and analytics to ensure that the microgrid operates efficiently and maintains a reliable supply of electricity, even when the availability of renewable energy sources varies due to changing weather conditions.